On a previous post we have successfully setup a Windows DNS Server. We have tested that we can successfully resolved a hostname (Router.theo.local) that we had freshly created, to an IP Address.
Some applications are heavily depend on the opposite scenario, where we request the hostname from the IP Address. Using the option a on the PING command we can test reverse scenario. We can see that the hostname cannot be resolved.
We actually need a Reverse Lookup Zone to make this working, which purpose is what we actually discussed. Turn IP Addresses to Hostnames. Go to "Reverse Lookup Zone" folder on DNS Application and create New Zone...
The wizard will start
We will create a primary zone (write mode) and store the Zone to AD. We will go into more depth about the Zone Types on a future Windows Server post. We will keep the DNS Server setup as simple as possible.
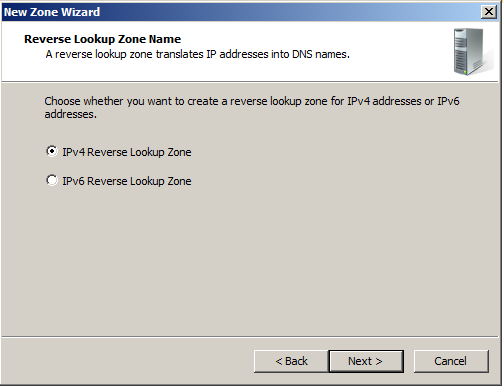
This is a IPv4 Zone
The network are currently using is 10.10.10.0/24, so we will specify: 10.10.10. Network ID
Now we have a subfolder under our main Reverse Lookup Zone folder.
We can create a PRT (Pointer Record) that points an IP Address to a hostname
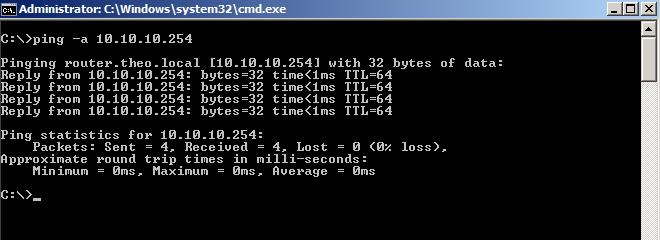
Now lets use the ping -a tool.
We can see that the hostname is resolved.
From now on if we create a new A record on the 10.10.10.0/24 range we can select to Create an associated PTR record
And the PTR record will be created automatically on the Reverse Lookup Zone section.
Some applications are heavily depend on the opposite scenario, where we request the hostname from the IP Address. Using the option a on the PING command we can test reverse scenario. We can see that the hostname cannot be resolved.
We actually need a Reverse Lookup Zone to make this working, which purpose is what we actually discussed. Turn IP Addresses to Hostnames. Go to "Reverse Lookup Zone" folder on DNS Application and create New Zone...
The wizard will start
We will create a primary zone (write mode) and store the Zone to AD. We will go into more depth about the Zone Types on a future Windows Server post. We will keep the DNS Server setup as simple as possible.
This is a IPv4 Zone
The network are currently using is 10.10.10.0/24, so we will specify: 10.10.10. Network ID
Now we have a subfolder under our main Reverse Lookup Zone folder.
We can create a PRT (Pointer Record) that points an IP Address to a hostname
Now lets use the ping -a tool.
We can see that the hostname is resolved.
From now on if we create a new A record on the 10.10.10.0/24 range we can select to Create an associated PTR record
And the PTR record will be created automatically on the Reverse Lookup Zone section.














No comments:
Post a Comment